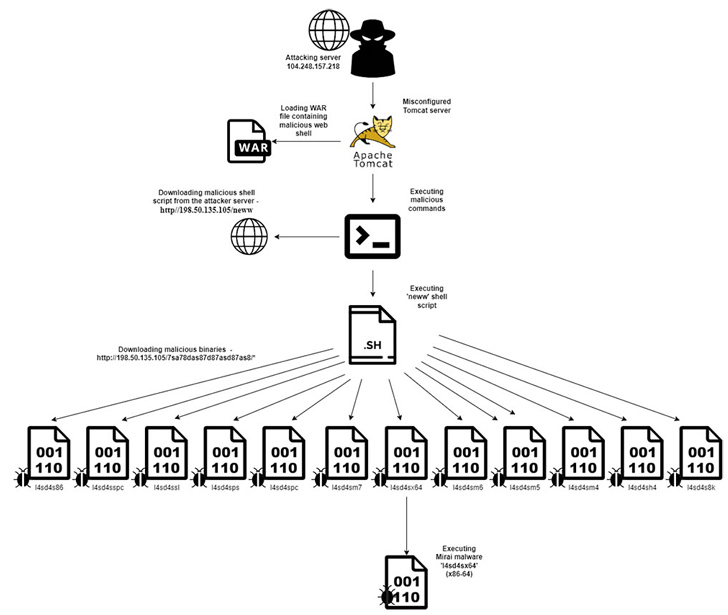
Misconfigured and poorly secured Apache Tomcat servers are being targeted as part of a new campaign designed to deliver the Mirai botnet malware and cryptocurrency miners.
The findings come courtesy of Aqua, which detected more than 800 attacks against its Tomcat server honeypots over a two-year time period, with 96% of the attacks linked to the Mirai botnet.
Of these attack attempts, 20% (or 152) entailed the use of a web shell script dubbed “neww” that originated from 24 unique IP addresses, with 68% of them originating from a single IP address (104.248.157[.]218).
Upon gaining a successful foothold, the threat actors have been observed deploying a WAR file that contains a malicious web shell class named ‘cmd.jsp’ that, in turn, is designed to listen to remote requests and execute arbitrary commands on the Tomcat server.
This includes downloading and running a shell script called “neww” after which the file is deleted using the “rm -rf” Linux command.

To mitigate against the ongoing campaign, it’s recommended that organizations secure their environments and follow credential hygiene to prevent brute-force attacks.
The development comes as the AhnLab Security Emergency Response Center (ASEC) reported that poorly managed MS-SQL servers are being breached to deploy a rootkit malware called Purple Fox, which acts as a loader to fetch additional malware such as coin miners.
These findings also demonstrate the lucrative nature of cryptocurrency mining, which has witnessed a 399% increase over last year, with 332 million cryptojacking attacks recorded in the first half of 2023 globally, according to SonicWall.
Source: https://thehackernews.com/